Nota
Haz clic aquí para descargar el código completo del ejemplo o para ejecutar este ejemplo en tu navegador a través de Binder
Clasificación de documentos de texto utilizando características dispersas¶
Este es un ejemplo que muestra cómo scikit-learn puede ser utilizado para clasificar documentos por temas utilizando un enfoque de bolsa de palabras (bag-of-words). Este ejemplo utiliza una matriz scipy.sparse para almacenar las características y demuestra varios clasificadores que pueden manejar eficientemente matrices dispersas.
El conjunto de datos utilizado en este ejemplo es el de 20 grupos de noticias(newsgroups). Se descargará automáticamente y se almacenará en la caché.
# Author: Peter Prettenhofer <peter.prettenhofer@gmail.com>
# Olivier Grisel <olivier.grisel@ensta.org>
# Mathieu Blondel <mathieu@mblondel.org>
# Lars Buitinck
# License: BSD 3 clause
import logging
import numpy as np
from optparse import OptionParser
import sys
from time import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import HashingVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectFromModel
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest, chi2
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeClassifier
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
from sklearn.linear_model import PassiveAggressiveClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import BernoulliNB, ComplementNB, MultinomialNB
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import NearestCentroid
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.utils.extmath import density
from sklearn import metrics
# Display progress logs on stdout
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(message)s')
op = OptionParser()
op.add_option("--report",
action="store_true", dest="print_report",
help="Print a detailed classification report.")
op.add_option("--chi2_select",
action="store", type="int", dest="select_chi2",
help="Select some number of features using a chi-squared test")
op.add_option("--confusion_matrix",
action="store_true", dest="print_cm",
help="Print the confusion matrix.")
op.add_option("--top10",
action="store_true", dest="print_top10",
help="Print ten most discriminative terms per class"
" for every classifier.")
op.add_option("--all_categories",
action="store_true", dest="all_categories",
help="Whether to use all categories or not.")
op.add_option("--use_hashing",
action="store_true",
help="Use a hashing vectorizer.")
op.add_option("--n_features",
action="store", type=int, default=2 ** 16,
help="n_features when using the hashing vectorizer.")
op.add_option("--filtered",
action="store_true",
help="Remove newsgroup information that is easily overfit: "
"headers, signatures, and quoting.")
def is_interactive():
return not hasattr(sys.modules['__main__'], '__file__')
# work-around for Jupyter notebook and IPython console
argv = [] if is_interactive() else sys.argv[1:]
(opts, args) = op.parse_args(argv)
if len(args) > 0:
op.error("this script takes no arguments.")
sys.exit(1)
print(__doc__)
op.print_help()
print()
Out:
Usage: plot_document_classification_20newsgroups.py [options]
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--report Print a detailed classification report.
--chi2_select=SELECT_CHI2
Select some number of features using a chi-squared
test
--confusion_matrix Print the confusion matrix.
--top10 Print ten most discriminative terms per class for
every classifier.
--all_categories Whether to use all categories or not.
--use_hashing Use a hashing vectorizer.
--n_features=N_FEATURES
n_features when using the hashing vectorizer.
--filtered Remove newsgroup information that is easily overfit:
headers, signatures, and quoting.
Carga los datos del conjunto de entrenamiento¶
Carguemos los datos del conjunto de datos de grupos de noticias(newsgroups), que comprende unos 18.000 artículos de grupos de noticias sobre 20 temas, divididos en dos subconjuntos: uno para el entrenamiento (o desarrollo) y otro para las pruebas (o para la evaluación del rendimiento).
if opts.all_categories:
categories = None
else:
categories = [
'alt.atheism',
'talk.religion.misc',
'comp.graphics',
'sci.space',
]
if opts.filtered:
remove = ('headers', 'footers', 'quotes')
else:
remove = ()
print("Loading 20 newsgroups dataset for categories:")
print(categories if categories else "all")
data_train = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='train', categories=categories,
shuffle=True, random_state=42,
remove=remove)
data_test = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='test', categories=categories,
shuffle=True, random_state=42,
remove=remove)
print('data loaded')
# order of labels in `target_names` can be different from `categories`
target_names = data_train.target_names
def size_mb(docs):
return sum(len(s.encode('utf-8')) for s in docs) / 1e6
data_train_size_mb = size_mb(data_train.data)
data_test_size_mb = size_mb(data_test.data)
print("%d documents - %0.3fMB (training set)" % (
len(data_train.data), data_train_size_mb))
print("%d documents - %0.3fMB (test set)" % (
len(data_test.data), data_test_size_mb))
print("%d categories" % len(target_names))
print()
# split a training set and a test set
y_train, y_test = data_train.target, data_test.target
print("Extracting features from the training data using a sparse vectorizer")
t0 = time()
if opts.use_hashing:
vectorizer = HashingVectorizer(stop_words='english', alternate_sign=False,
n_features=opts.n_features)
X_train = vectorizer.transform(data_train.data)
else:
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(sublinear_tf=True, max_df=0.5,
stop_words='english')
X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(data_train.data)
duration = time() - t0
print("done in %fs at %0.3fMB/s" % (duration, data_train_size_mb / duration))
print("n_samples: %d, n_features: %d" % X_train.shape)
print()
print("Extracting features from the test data using the same vectorizer")
t0 = time()
X_test = vectorizer.transform(data_test.data)
duration = time() - t0
print("done in %fs at %0.3fMB/s" % (duration, data_test_size_mb / duration))
print("n_samples: %d, n_features: %d" % X_test.shape)
print()
# mapping from integer feature name to original token string
if opts.use_hashing:
feature_names = None
else:
feature_names = vectorizer.get_feature_names()
if opts.select_chi2:
print("Extracting %d best features by a chi-squared test" %
opts.select_chi2)
t0 = time()
ch2 = SelectKBest(chi2, k=opts.select_chi2)
X_train = ch2.fit_transform(X_train, y_train)
X_test = ch2.transform(X_test)
if feature_names:
# keep selected feature names
feature_names = [feature_names[i] for i
in ch2.get_support(indices=True)]
print("done in %fs" % (time() - t0))
print()
if feature_names:
feature_names = np.asarray(feature_names)
def trim(s):
"""Trim string to fit on terminal (assuming 80-column display)"""
return s if len(s) <= 80 else s[:77] + "..."
Out:
Loading 20 newsgroups dataset for categories:
['alt.atheism', 'talk.religion.misc', 'comp.graphics', 'sci.space']
data loaded
2034 documents - 3.980MB (training set)
1353 documents - 2.867MB (test set)
4 categories
Extracting features from the training data using a sparse vectorizer
done in 0.527362s at 7.546MB/s
n_samples: 2034, n_features: 33809
Extracting features from the test data using the same vectorizer
done in 0.350521s at 8.181MB/s
n_samples: 1353, n_features: 33809
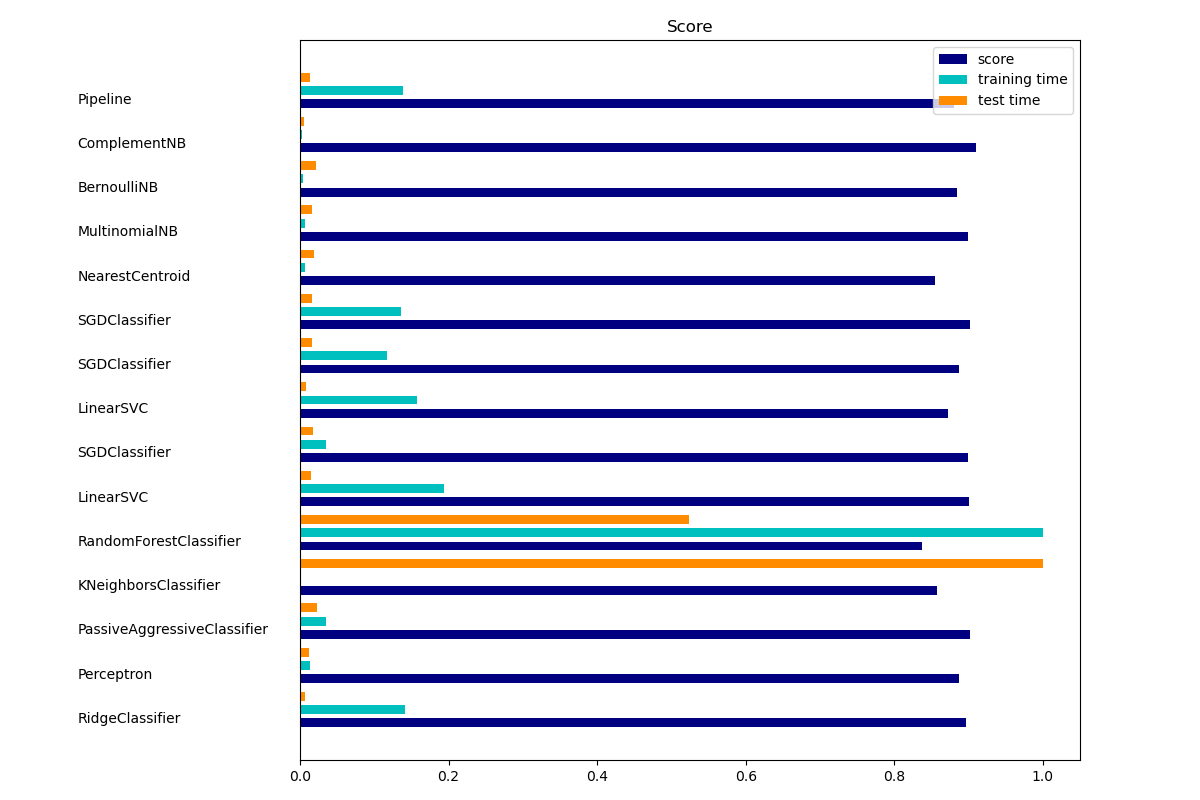
Clasificadores de rendimiento¶
Entrenamos y probamos los conjuntos de datos con 15 modelos de clasificación diferentes y obtenemos resultados de rendimiento para cada modelo.
def benchmark(clf):
print('_' * 80)
print("Training: ")
print(clf)
t0 = time()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_time = time() - t0
print("train time: %0.3fs" % train_time)
t0 = time()
pred = clf.predict(X_test)
test_time = time() - t0
print("test time: %0.3fs" % test_time)
score = metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, pred)
print("accuracy: %0.3f" % score)
if hasattr(clf, 'coef_'):
print("dimensionality: %d" % clf.coef_.shape[1])
print("density: %f" % density(clf.coef_))
if opts.print_top10 and feature_names is not None:
print("top 10 keywords per class:")
for i, label in enumerate(target_names):
top10 = np.argsort(clf.coef_[i])[-10:]
print(trim("%s: %s" % (label, " ".join(feature_names[top10]))))
print()
if opts.print_report:
print("classification report:")
print(metrics.classification_report(y_test, pred,
target_names=target_names))
if opts.print_cm:
print("confusion matrix:")
print(metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test, pred))
print()
clf_descr = str(clf).split('(')[0]
return clf_descr, score, train_time, test_time
results = []
for clf, name in (
(RidgeClassifier(tol=1e-2, solver="sag"), "Ridge Classifier"),
(Perceptron(max_iter=50), "Perceptron"),
(PassiveAggressiveClassifier(max_iter=50),
"Passive-Aggressive"),
(KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=10), "kNN"),
(RandomForestClassifier(), "Random forest")):
print('=' * 80)
print(name)
results.append(benchmark(clf))
for penalty in ["l2", "l1"]:
print('=' * 80)
print("%s penalty" % penalty.upper())
# Train Liblinear model
results.append(benchmark(LinearSVC(penalty=penalty, dual=False,
tol=1e-3)))
# Train SGD model
results.append(benchmark(SGDClassifier(alpha=.0001, max_iter=50,
penalty=penalty)))
# Train SGD with Elastic Net penalty
print('=' * 80)
print("Elastic-Net penalty")
results.append(benchmark(SGDClassifier(alpha=.0001, max_iter=50,
penalty="elasticnet")))
# Train NearestCentroid without threshold
print('=' * 80)
print("NearestCentroid (aka Rocchio classifier)")
results.append(benchmark(NearestCentroid()))
# Train sparse Naive Bayes classifiers
print('=' * 80)
print("Naive Bayes")
results.append(benchmark(MultinomialNB(alpha=.01)))
results.append(benchmark(BernoulliNB(alpha=.01)))
results.append(benchmark(ComplementNB(alpha=.1)))
print('=' * 80)
print("LinearSVC with L1-based feature selection")
# The smaller C, the stronger the regularization.
# The more regularization, the more sparsity.
results.append(benchmark(Pipeline([
('feature_selection', SelectFromModel(LinearSVC(penalty="l1", dual=False,
tol=1e-3))),
('classification', LinearSVC(penalty="l2"))])))
Out:
================================================================================
Ridge Classifier
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
RidgeClassifier(solver='sag', tol=0.01)
/home/mapologo/miniconda3/envs/sklearn/lib/python3.9/site-packages/scikit_learn-0.24.1-py3.9-linux-x86_64.egg/sklearn/linear_model/_ridge.py:555: UserWarning: "sag" solver requires many iterations to fit an intercept with sparse inputs. Either set the solver to "auto" or "sparse_cg", or set a low "tol" and a high "max_iter" (especially if inputs are not standardized).
warnings.warn(
train time: 0.249s
test time: 0.001s
accuracy: 0.897
dimensionality: 33809
density: 1.000000
================================================================================
Perceptron
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
Perceptron(max_iter=50)
train time: 0.024s
test time: 0.003s
accuracy: 0.888
dimensionality: 33809
density: 0.255302
================================================================================
Passive-Aggressive
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
PassiveAggressiveClassifier(max_iter=50)
train time: 0.063s
test time: 0.005s
accuracy: 0.902
dimensionality: 33809
density: 0.692841
================================================================================
kNN
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=10)
train time: 0.003s
test time: 0.231s
accuracy: 0.858
================================================================================
Random forest
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
RandomForestClassifier()
train time: 1.761s
test time: 0.121s
accuracy: 0.837
================================================================================
L2 penalty
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
LinearSVC(dual=False, tol=0.001)
train time: 0.342s
test time: 0.003s
accuracy: 0.900
dimensionality: 33809
density: 1.000000
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
SGDClassifier(max_iter=50)
train time: 0.061s
test time: 0.004s
accuracy: 0.899
dimensionality: 33809
density: 0.569944
================================================================================
L1 penalty
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
LinearSVC(dual=False, penalty='l1', tol=0.001)
train time: 0.278s
test time: 0.002s
accuracy: 0.873
dimensionality: 33809
density: 0.005561
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
SGDClassifier(max_iter=50, penalty='l1')
train time: 0.207s
test time: 0.004s
accuracy: 0.888
dimensionality: 33809
density: 0.022982
================================================================================
Elastic-Net penalty
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
SGDClassifier(max_iter=50, penalty='elasticnet')
train time: 0.239s
test time: 0.004s
accuracy: 0.902
dimensionality: 33809
density: 0.187502
================================================================================
NearestCentroid (aka Rocchio classifier)
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
NearestCentroid()
train time: 0.011s
test time: 0.004s
accuracy: 0.855
================================================================================
Naive Bayes
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
MultinomialNB(alpha=0.01)
train time: 0.012s
test time: 0.004s
accuracy: 0.899
/home/mapologo/miniconda3/envs/sklearn/lib/python3.9/site-packages/scikit_learn-0.24.1-py3.9-linux-x86_64.egg/sklearn/utils/deprecation.py:101: FutureWarning: Attribute coef_ was deprecated in version 0.24 and will be removed in 1.1 (renaming of 0.26).
warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning)
dimensionality: 33809
density: 1.000000
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
BernoulliNB(alpha=0.01)
train time: 0.007s
test time: 0.005s
accuracy: 0.884
/home/mapologo/miniconda3/envs/sklearn/lib/python3.9/site-packages/scikit_learn-0.24.1-py3.9-linux-x86_64.egg/sklearn/utils/deprecation.py:101: FutureWarning: Attribute coef_ was deprecated in version 0.24 and will be removed in 1.1 (renaming of 0.26).
warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning)
dimensionality: 33809
density: 1.000000
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
ComplementNB(alpha=0.1)
train time: 0.005s
test time: 0.001s
accuracy: 0.911
/home/mapologo/miniconda3/envs/sklearn/lib/python3.9/site-packages/scikit_learn-0.24.1-py3.9-linux-x86_64.egg/sklearn/utils/deprecation.py:101: FutureWarning: Attribute coef_ was deprecated in version 0.24 and will be removed in 1.1 (renaming of 0.26).
warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning)
dimensionality: 33809
density: 1.000000
================================================================================
LinearSVC with L1-based feature selection
________________________________________________________________________________
Training:
Pipeline(steps=[('feature_selection',
SelectFromModel(estimator=LinearSVC(dual=False, penalty='l1',
tol=0.001))),
('classification', LinearSVC())])
train time: 0.244s
test time: 0.003s
accuracy: 0.880
Añadir gráficos¶
El gráfico de barras indica la exactitud, el tiempo de entrenamiento (normalizado) y el tiempo de prueba (normalizado) de cada clasificador.
indices = np.arange(len(results))
results = [[x[i] for x in results] for i in range(4)]
clf_names, score, training_time, test_time = results
training_time = np.array(training_time) / np.max(training_time)
test_time = np.array(test_time) / np.max(test_time)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.title("Score")
plt.barh(indices, score, .2, label="score", color='navy')
plt.barh(indices + .3, training_time, .2, label="training time",
color='c')
plt.barh(indices + .6, test_time, .2, label="test time", color='darkorange')
plt.yticks(())
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplots_adjust(left=.25)
plt.subplots_adjust(top=.95)
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=.05)
for i, c in zip(indices, clf_names):
plt.text(-.3, i, c)
plt.show()
Tiempo total de ejecución del script: (0 minutos 5.632 segundos)
