Nota
Haz clic aquí para descargar el código de ejemplo completo o para ejecutar este ejemplo en tu navegador a través de Binder
SVM de una clase con núcleo no lineal (RBF)¶
Un ejemplo utilizando un SVM de una clase para la detección de novedades.
El SVM de una clase es un algoritmo no supervisado que aprende una función de decisión para la detección de novedades: clasificar los nuevos datos como similares o diferentes al conjunto de entrenamiento.
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.font_manager
from sklearn import svm
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-5, 5, 500), np.linspace(-5, 5, 500))
# Generate train data
X = 0.3 * np.random.randn(100, 2)
X_train = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
# Generate some regular novel observations
X = 0.3 * np.random.randn(20, 2)
X_test = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
# Generate some abnormal novel observations
X_outliers = np.random.uniform(low=-4, high=4, size=(20, 2))
# fit the model
clf = svm.OneClassSVM(nu=0.1, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.1)
clf.fit(X_train)
y_pred_train = clf.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test = clf.predict(X_test)
y_pred_outliers = clf.predict(X_outliers)
n_error_train = y_pred_train[y_pred_train == -1].size
n_error_test = y_pred_test[y_pred_test == -1].size
n_error_outliers = y_pred_outliers[y_pred_outliers == 1].size
# plot the line, the points, and the nearest vectors to the plane
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
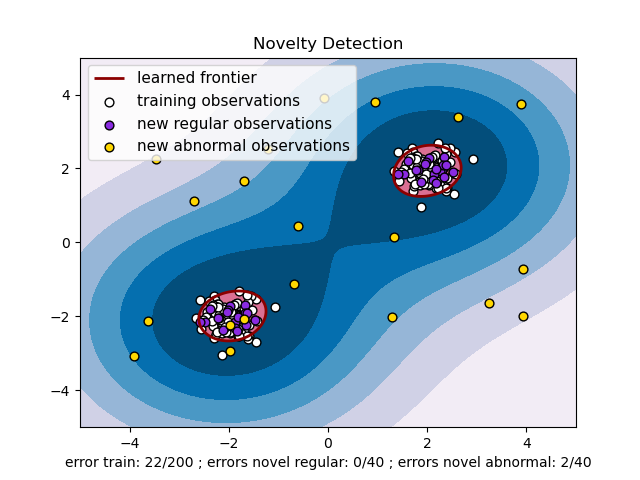
plt.title("Novelty Detection")
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=np.linspace(Z.min(), 0, 7), cmap=plt.cm.PuBu)
a = plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linewidths=2, colors='darkred')
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0, Z.max()], colors='palevioletred')
s = 40
b1 = plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c='white', s=s, edgecolors='k')
b2 = plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c='blueviolet', s=s,
edgecolors='k')
c = plt.scatter(X_outliers[:, 0], X_outliers[:, 1], c='gold', s=s,
edgecolors='k')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlim((-5, 5))
plt.ylim((-5, 5))
plt.legend([a.collections[0], b1, b2, c],
["learned frontier", "training observations",
"new regular observations", "new abnormal observations"],
loc="upper left",
prop=matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties(size=11))
plt.xlabel(
"error train: %d/200 ; errors novel regular: %d/40 ; "
"errors novel abnormal: %d/40"
% (n_error_train, n_error_test, n_error_outliers))
plt.show()
Tiempo total de ejecución del script: (0 minutos 0.500 segundos)
