Nota
Haga clic en aquí para descargar el código completo del ejemplo o para ejecutar este ejemplo en su navegador a través de Binder
Comparación de clasificadores¶
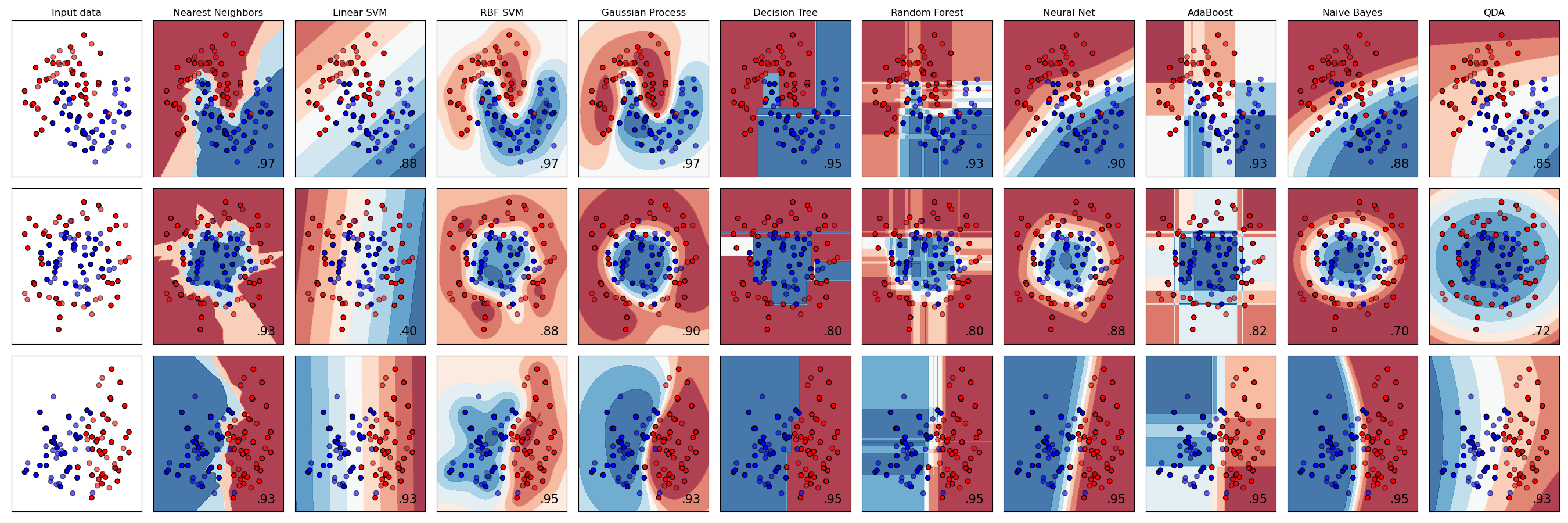
Una comparación de varios clasificadores en scikit-learn en conjuntos de datos sintéticos. El objetivo de este ejemplo es ilustrar la naturaleza de los límites de decisión de los diferentes clasificadores. Hay que tomarlo con pinzas, ya que la intuición que transmiten estos ejemplos no se traslada necesariamente a los conjuntos de datos reales.
Especialmente en los espacios de alta dimensión, los datos pueden separarse más fácilmente de forma lineal y la simplicidad de clasificadores como el Bayes ingenuo y el SVM lineal podría conducir a una mejor generalización que la que se consigue con otros clasificadores.
Los gráficos muestran los puntos de entrenamiento en colores sólidos y los puntos de prueba semitransparentes. La parte inferior derecha muestra la precisión de la clasificación en el conjunto de pruebas.
print(__doc__)
# Code source: Gaël Varoquaux
# Andreas Müller
# Modified for documentation by Jaques Grobler
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons, make_circles, make_classification
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessClassifier
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import RBF
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
names = ["Nearest Neighbors", "Linear SVM", "RBF SVM", "Gaussian Process",
"Decision Tree", "Random Forest", "Neural Net", "AdaBoost",
"Naive Bayes", "QDA"]
classifiers = [
KNeighborsClassifier(3),
SVC(kernel="linear", C=0.025),
SVC(gamma=2, C=1),
GaussianProcessClassifier(1.0 * RBF(1.0)),
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5),
RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5, n_estimators=10, max_features=1),
MLPClassifier(alpha=1, max_iter=1000),
AdaBoostClassifier(),
GaussianNB(),
QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis()]
X, y = make_classification(n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2,
random_state=1, n_clusters_per_class=1)
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
X += 2 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
linearly_separable = (X, y)
datasets = [make_moons(noise=0.3, random_state=0),
make_circles(noise=0.2, factor=0.5, random_state=1),
linearly_separable
]
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(27, 9))
i = 1
# iterate over datasets
for ds_cnt, ds in enumerate(datasets):
# preprocess dataset, split into training and test part
X, y = ds
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = \
train_test_split(X, y, test_size=.4, random_state=42)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# just plot the dataset first
cm = plt.cm.RdBu
cm_bright = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#0000FF'])
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
if ds_cnt == 0:
ax.set_title("Input data")
# Plot the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright,
edgecolors='k')
# Plot the testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6,
edgecolors='k')
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
i += 1
# iterate over classifiers
for name, clf in zip(names, classifiers):
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = clf.score(X_test, y_test)
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max].
if hasattr(clf, "decision_function"):
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
else:
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1]
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cm, alpha=.8)
# Plot the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright,
edgecolors='k')
# Plot the testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright,
edgecolors='k', alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
if ds_cnt == 0:
ax.set_title(name)
ax.text(xx.max() - .3, yy.min() + .3, ('%.2f' % score).lstrip('0'),
size=15, horizontalalignment='right')
i += 1
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Tiempo total de ejecución del script: (0 minutos 7.357 segundos)
