Nota
Haga clic en aquí para descargar el código completo del ejemplo o para ejecutar este ejemplo en su navegador a través de Binder
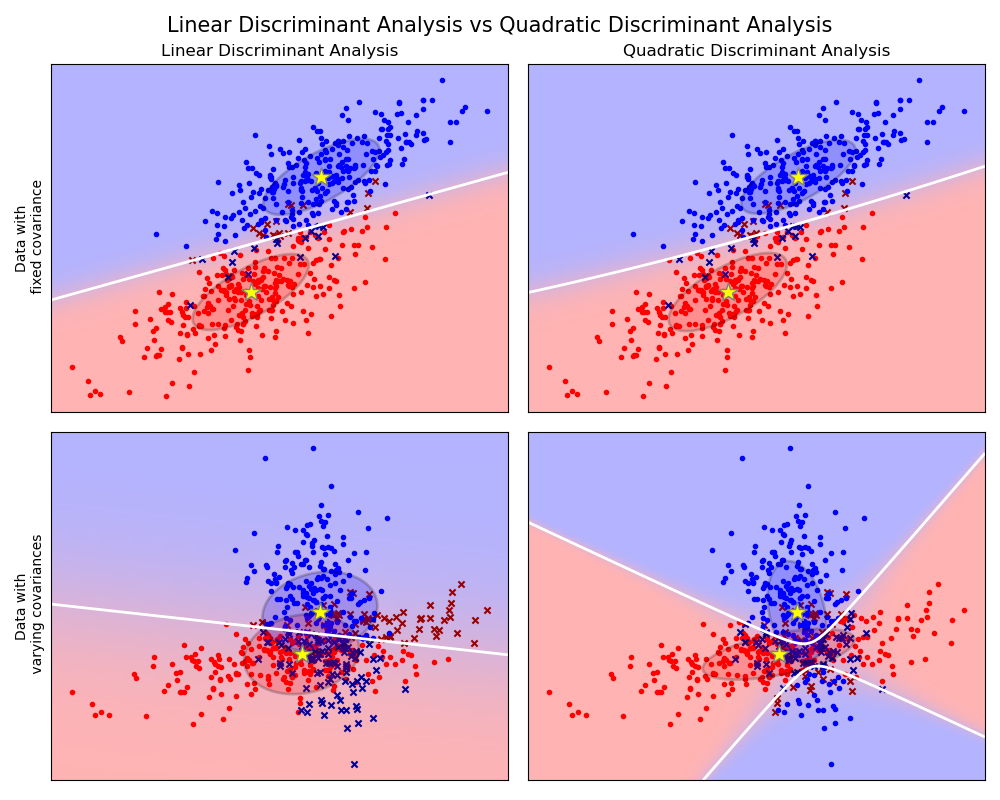
Análisis discriminante lineal y cuadrático con elipsoide de covarianza¶
Este ejemplo traza los elipsoides de covarianza de cada clase y límite de decisión aprendidos por LDA y QDA. Los elipsoides muestran la doble desviación estándar de cada clase. Con LDA, la desviación estándar es la misma para todas las clases, mientras que cada clase tiene su propia desviación estándar con QDA.
Out:
/home/mapologo/Descargas/scikit-learn-0.24.X/examples/classification/plot_lda_qda.py:93: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: shading='flat' when X and Y have the same dimensions as C is deprecated since 3.3. Either specify the corners of the quadrilaterals with X and Y, or pass shading='auto', 'nearest' or 'gouraud', or set rcParams['pcolor.shading']. This will become an error two minor releases later.
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap='red_blue_classes',
/home/mapologo/Descargas/scikit-learn-0.24.X/examples/classification/plot_lda_qda.py:93: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: shading='flat' when X and Y have the same dimensions as C is deprecated since 3.3. Either specify the corners of the quadrilaterals with X and Y, or pass shading='auto', 'nearest' or 'gouraud', or set rcParams['pcolor.shading']. This will become an error two minor releases later.
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap='red_blue_classes',
/home/mapologo/Descargas/scikit-learn-0.24.X/examples/classification/plot_lda_qda.py:93: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: shading='flat' when X and Y have the same dimensions as C is deprecated since 3.3. Either specify the corners of the quadrilaterals with X and Y, or pass shading='auto', 'nearest' or 'gouraud', or set rcParams['pcolor.shading']. This will become an error two minor releases later.
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap='red_blue_classes',
/home/mapologo/Descargas/scikit-learn-0.24.X/examples/classification/plot_lda_qda.py:93: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: shading='flat' when X and Y have the same dimensions as C is deprecated since 3.3. Either specify the corners of the quadrilaterals with X and Y, or pass shading='auto', 'nearest' or 'gouraud', or set rcParams['pcolor.shading']. This will become an error two minor releases later.
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap='red_blue_classes',
print(__doc__)
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import colors
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis
# #############################################################################
# Colormap
cmap = colors.LinearSegmentedColormap(
'red_blue_classes',
{'red': [(0, 1, 1), (1, 0.7, 0.7)],
'green': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 0.7, 0.7)],
'blue': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 1, 1)]})
plt.cm.register_cmap(cmap=cmap)
# #############################################################################
# Generate datasets
def dataset_fixed_cov():
'''Generate 2 Gaussians samples with the same covariance matrix'''
n, dim = 300, 2
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0., -0.23], [0.83, .23]])
X = np.r_[np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C),
np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C) + np.array([1, 1])]
y = np.hstack((np.zeros(n), np.ones(n)))
return X, y
def dataset_cov():
'''Generate 2 Gaussians samples with different covariance matrices'''
n, dim = 300, 2
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0., -1.], [2.5, .7]]) * 2.
X = np.r_[np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C),
np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C.T) + np.array([1, 4])]
y = np.hstack((np.zeros(n), np.ones(n)))
return X, y
# #############################################################################
# Plot functions
def plot_data(lda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index):
splot = plt.subplot(2, 2, fig_index)
if fig_index == 1:
plt.title('Linear Discriminant Analysis')
plt.ylabel('Data with\n fixed covariance')
elif fig_index == 2:
plt.title('Quadratic Discriminant Analysis')
elif fig_index == 3:
plt.ylabel('Data with\n varying covariances')
tp = (y == y_pred) # True Positive
tp0, tp1 = tp[y == 0], tp[y == 1]
X0, X1 = X[y == 0], X[y == 1]
X0_tp, X0_fp = X0[tp0], X0[~tp0]
X1_tp, X1_fp = X1[tp1], X1[~tp1]
# class 0: dots
plt.scatter(X0_tp[:, 0], X0_tp[:, 1], marker='.', color='red')
plt.scatter(X0_fp[:, 0], X0_fp[:, 1], marker='x',
s=20, color='#990000') # dark red
# class 1: dots
plt.scatter(X1_tp[:, 0], X1_tp[:, 1], marker='.', color='blue')
plt.scatter(X1_fp[:, 0], X1_fp[:, 1], marker='x',
s=20, color='#000099') # dark blue
# class 0 and 1 : areas
nx, ny = 200, 100
x_min, x_max = plt.xlim()
y_min, y_max = plt.ylim()
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, nx),
np.linspace(y_min, y_max, ny))
Z = lda.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z[:, 1].reshape(xx.shape)
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap='red_blue_classes',
norm=colors.Normalize(0., 1.), zorder=0)
plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, [0.5], linewidths=2., colors='white')
# means
plt.plot(lda.means_[0][0], lda.means_[0][1],
'*', color='yellow', markersize=15, markeredgecolor='grey')
plt.plot(lda.means_[1][0], lda.means_[1][1],
'*', color='yellow', markersize=15, markeredgecolor='grey')
return splot
def plot_ellipse(splot, mean, cov, color):
v, w = linalg.eigh(cov)
u = w[0] / linalg.norm(w[0])
angle = np.arctan(u[1] / u[0])
angle = 180 * angle / np.pi # convert to degrees
# filled Gaussian at 2 standard deviation
ell = mpl.patches.Ellipse(mean, 2 * v[0] ** 0.5, 2 * v[1] ** 0.5,
180 + angle, facecolor=color,
edgecolor='black', linewidth=2)
ell.set_clip_box(splot.bbox)
ell.set_alpha(0.2)
splot.add_artist(ell)
splot.set_xticks(())
splot.set_yticks(())
def plot_lda_cov(lda, splot):
plot_ellipse(splot, lda.means_[0], lda.covariance_, 'red')
plot_ellipse(splot, lda.means_[1], lda.covariance_, 'blue')
def plot_qda_cov(qda, splot):
plot_ellipse(splot, qda.means_[0], qda.covariance_[0], 'red')
plot_ellipse(splot, qda.means_[1], qda.covariance_[1], 'blue')
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8), facecolor='white')
plt.suptitle('Linear Discriminant Analysis vs Quadratic Discriminant Analysis',
y=0.98, fontsize=15)
for i, (X, y) in enumerate([dataset_fixed_cov(), dataset_cov()]):
# Linear Discriminant Analysis
lda = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(solver="svd", store_covariance=True)
y_pred = lda.fit(X, y).predict(X)
splot = plot_data(lda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index=2 * i + 1)
plot_lda_cov(lda, splot)
plt.axis('tight')
# Quadratic Discriminant Analysis
qda = QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis(store_covariance=True)
y_pred = qda.fit(X, y).predict(X)
splot = plot_data(qda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index=2 * i + 2)
plot_qda_cov(qda, splot)
plt.axis('tight')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.92)
plt.show()
Tiempo total de ejecución del script: (0 minutos 0.600 segundos)
