Nota
Haz clic en aquí para descargar el código de ejemplo completo o para ejecutar este ejemplo en tu navegador a través de Binder
Desnaturalización de imágenes mediante el aprendizaje de diccionarios¶
Un ejemplo en el que se compara el efecto de reconstruir fragmentos ruidosos de una imagen de la cara de un mapache utilizando primero Diccionario de aprrendizaje en línea y varios métodos de transformación.
El diccionario se ajusta a la mitad izquierda de la imagen distorsionada, y posteriormente se utiliza para reconstruir la mitad derecha. Hay que tener en cuenta que se podría conseguir un rendimiento aún mayor ajustando una imagen no distorsionada (es decir, sin ruido), pero aquí partimos de la base de que no está disponible.
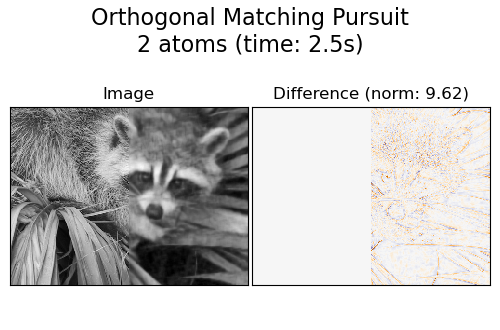
Una práctica habitual para evaluar los resultados de la eliminación de ruido de las imágenes es observar la diferencia entre la reconstrucción y la imagen original. Si la reconstrucción es perfecta, se verá como un ruido gaussiano.
Se puede ver en los gráficos que los resultados de Búsqueda de coincidencias ortogonales (OMP) con dos coeficientes distintos de cero están un poco menos sesgados que cuando se mantiene sólo uno (las aristas parecen menos prominentes). Además, está más cerca de la verdad fundamental en la norma de Frobenius.
El resultado de Regresión de ángulo mínimo está mucho más sesgado: la diferencia recuerda al valor de intensidad local de la imagen original.
Está claro que fijar umbrales no es útil para la eliminación de ruido, pero aquí se muestra que puede producir una salida sugerente con una velocidad muy alta, y por lo tanto ser útil para otras tareas como la clasificación de objetos, donde el rendimiento no está necesariamente relacionado con la visualización.
Out:
Distorting image...
Extracting reference patches...
done in 0.01s.
Learning the dictionary...
done in 13.44s.
Extracting noisy patches...
done in 0.01s.
Orthogonal Matching Pursuit
1 atom...
done in 1.47s.
Orthogonal Matching Pursuit
2 atoms...
done in 2.49s.
Least-angle regression
5 atoms...
done in 26.76s.
Thresholding
alpha=0.1...
done in 0.23s.
print(__doc__)
from time import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
from sklearn.decomposition import MiniBatchDictionaryLearning
from sklearn.feature_extraction.image import extract_patches_2d
from sklearn.feature_extraction.image import reconstruct_from_patches_2d
try: # SciPy >= 0.16 have face in misc
from scipy.misc import face
face = face(gray=True)
except ImportError:
face = sp.face(gray=True)
# Convert from uint8 representation with values between 0 and 255 to
# a floating point representation with values between 0 and 1.
face = face / 255.
# downsample for higher speed
face = face[::4, ::4] + face[1::4, ::4] + face[::4, 1::4] + face[1::4, 1::4]
face /= 4.0
height, width = face.shape
# Distort the right half of the image
print('Distorting image...')
distorted = face.copy()
distorted[:, width // 2:] += 0.075 * np.random.randn(height, width // 2)
# Extract all reference patches from the left half of the image
print('Extracting reference patches...')
t0 = time()
patch_size = (7, 7)
data = extract_patches_2d(distorted[:, :width // 2], patch_size)
data = data.reshape(data.shape[0], -1)
data -= np.mean(data, axis=0)
data /= np.std(data, axis=0)
print('done in %.2fs.' % (time() - t0))
# #############################################################################
# Learn the dictionary from reference patches
print('Learning the dictionary...')
t0 = time()
dico = MiniBatchDictionaryLearning(n_components=100, alpha=1, n_iter=500)
V = dico.fit(data).components_
dt = time() - t0
print('done in %.2fs.' % dt)
plt.figure(figsize=(4.2, 4))
for i, comp in enumerate(V[:100]):
plt.subplot(10, 10, i + 1)
plt.imshow(comp.reshape(patch_size), cmap=plt.cm.gray_r,
interpolation='nearest')
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.suptitle('Dictionary learned from face patches\n' +
'Train time %.1fs on %d patches' % (dt, len(data)),
fontsize=16)
plt.subplots_adjust(0.08, 0.02, 0.92, 0.85, 0.08, 0.23)
# #############################################################################
# Display the distorted image
def show_with_diff(image, reference, title):
"""Helper function to display denoising"""
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 3.3))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.title('Image')
plt.imshow(image, vmin=0, vmax=1, cmap=plt.cm.gray,
interpolation='nearest')
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
difference = image - reference
plt.title('Difference (norm: %.2f)' % np.sqrt(np.sum(difference ** 2)))
plt.imshow(difference, vmin=-0.5, vmax=0.5, cmap=plt.cm.PuOr,
interpolation='nearest')
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.suptitle(title, size=16)
plt.subplots_adjust(0.02, 0.02, 0.98, 0.79, 0.02, 0.2)
show_with_diff(distorted, face, 'Distorted image')
# #############################################################################
# Extract noisy patches and reconstruct them using the dictionary
print('Extracting noisy patches... ')
t0 = time()
data = extract_patches_2d(distorted[:, width // 2:], patch_size)
data = data.reshape(data.shape[0], -1)
intercept = np.mean(data, axis=0)
data -= intercept
print('done in %.2fs.' % (time() - t0))
transform_algorithms = [
('Orthogonal Matching Pursuit\n1 atom', 'omp',
{'transform_n_nonzero_coefs': 1}),
('Orthogonal Matching Pursuit\n2 atoms', 'omp',
{'transform_n_nonzero_coefs': 2}),
('Least-angle regression\n5 atoms', 'lars',
{'transform_n_nonzero_coefs': 5}),
('Thresholding\n alpha=0.1', 'threshold', {'transform_alpha': .1})]
reconstructions = {}
for title, transform_algorithm, kwargs in transform_algorithms:
print(title + '...')
reconstructions[title] = face.copy()
t0 = time()
dico.set_params(transform_algorithm=transform_algorithm, **kwargs)
code = dico.transform(data)
patches = np.dot(code, V)
patches += intercept
patches = patches.reshape(len(data), *patch_size)
if transform_algorithm == 'threshold':
patches -= patches.min()
patches /= patches.max()
reconstructions[title][:, width // 2:] = reconstruct_from_patches_2d(
patches, (height, width // 2))
dt = time() - t0
print('done in %.2fs.' % dt)
show_with_diff(reconstructions[title], face,
title + ' (time: %.1fs)' % dt)
plt.show()
Tiempo total de ejecución del script: (0 minutos 48.461 segundos)