Nota
Haz clic aquí para descargar el código completo del ejemplo o para ejecutar este ejemplo en tu navegador a través de Binder
Agrupamiento de características vs. selección univariante¶
Este ejemplo compara 2 estrategias de reducción de dimensionalidad:
selección de características univariantes con Anova
aglomeración de características con el agrupamiento jerárquico de Ward
Ambos métodos se comparan en un problema de regresión utilizando un BayesianRidge como estimador supervisado.
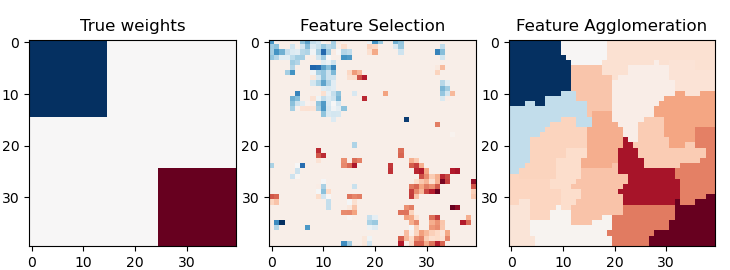
Out:
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.cluster._agglomerative.ward_tree...
ward_tree(array([[-0.451933, ..., -0.675318],
...,
[ 0.275706, ..., -1.085711]]), connectivity=<1600x1600 sparse matrix of type '<class 'numpy.int64'>'
with 7840 stored elements in COOrdinate format>, n_clusters=None, return_distance=False)
________________________________________________________ward_tree - 0.1s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.cluster._agglomerative.ward_tree...
ward_tree(array([[ 0.905206, ..., 0.161245],
...,
[-0.849835, ..., -1.091621]]), connectivity=<1600x1600 sparse matrix of type '<class 'numpy.int64'>'
with 7840 stored elements in COOrdinate format>, n_clusters=None, return_distance=False)
________________________________________________________ward_tree - 0.1s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.cluster._agglomerative.ward_tree...
ward_tree(array([[ 0.905206, ..., -0.675318],
...,
[-0.849835, ..., -1.085711]]), connectivity=<1600x1600 sparse matrix of type '<class 'numpy.int64'>'
with 7840 stored elements in COOrdinate format>, n_clusters=None, return_distance=False)
________________________________________________________ward_tree - 0.1s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.feature_selection._univariate_selection.f_regression...
f_regression(array([[-0.451933, ..., 0.275706],
...,
[-0.675318, ..., -1.085711]]),
array([ 25.267703, ..., -25.026711]))
_____________________________________________________f_regression - 0.0s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.feature_selection._univariate_selection.f_regression...
f_regression(array([[ 0.905206, ..., -0.849835],
...,
[ 0.161245, ..., -1.091621]]),
array([ -27.447268, ..., -112.638768]))
_____________________________________________________f_regression - 0.0s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.feature_selection._univariate_selection.f_regression...
f_regression(array([[ 0.905206, ..., -0.849835],
...,
[-0.675318, ..., -1.085711]]),
array([-27.447268, ..., -25.026711]))
_____________________________________________________f_regression - 0.0s, 0.0min
# Author: Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
# License: BSD 3 clause
print(__doc__)
import shutil
import tempfile
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import linalg, ndimage
from joblib import Memory
from sklearn.feature_extraction.image import grid_to_graph
from sklearn import feature_selection
from sklearn.cluster import FeatureAgglomeration
from sklearn.linear_model import BayesianRidge
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
# #############################################################################
# Generate data
n_samples = 200
size = 40 # image size
roi_size = 15
snr = 5.
np.random.seed(0)
mask = np.ones([size, size], dtype=bool)
coef = np.zeros((size, size))
coef[0:roi_size, 0:roi_size] = -1.
coef[-roi_size:, -roi_size:] = 1.
X = np.random.randn(n_samples, size ** 2)
for x in X: # smooth data
x[:] = ndimage.gaussian_filter(x.reshape(size, size), sigma=1.0).ravel()
X -= X.mean(axis=0)
X /= X.std(axis=0)
y = np.dot(X, coef.ravel())
noise = np.random.randn(y.shape[0])
noise_coef = (linalg.norm(y, 2) / np.exp(snr / 20.)) / linalg.norm(noise, 2)
y += noise_coef * noise # add noise
# #############################################################################
# Compute the coefs of a Bayesian Ridge with GridSearch
cv = KFold(2) # cross-validation generator for model selection
ridge = BayesianRidge()
cachedir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
mem = Memory(location=cachedir, verbose=1)
# Ward agglomeration followed by BayesianRidge
connectivity = grid_to_graph(n_x=size, n_y=size)
ward = FeatureAgglomeration(n_clusters=10, connectivity=connectivity,
memory=mem)
clf = Pipeline([('ward', ward), ('ridge', ridge)])
# Select the optimal number of parcels with grid search
clf = GridSearchCV(clf, {'ward__n_clusters': [10, 20, 30]}, n_jobs=1, cv=cv)
clf.fit(X, y) # set the best parameters
coef_ = clf.best_estimator_.steps[-1][1].coef_
coef_ = clf.best_estimator_.steps[0][1].inverse_transform(coef_)
coef_agglomeration_ = coef_.reshape(size, size)
# Anova univariate feature selection followed by BayesianRidge
f_regression = mem.cache(feature_selection.f_regression) # caching function
anova = feature_selection.SelectPercentile(f_regression)
clf = Pipeline([('anova', anova), ('ridge', ridge)])
# Select the optimal percentage of features with grid search
clf = GridSearchCV(clf, {'anova__percentile': [5, 10, 20]}, cv=cv)
clf.fit(X, y) # set the best parameters
coef_ = clf.best_estimator_.steps[-1][1].coef_
coef_ = clf.best_estimator_.steps[0][1].inverse_transform(coef_.reshape(1, -1))
coef_selection_ = coef_.reshape(size, size)
# #############################################################################
# Inverse the transformation to plot the results on an image
plt.close('all')
plt.figure(figsize=(7.3, 2.7))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(coef, interpolation="nearest", cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r)
plt.title("True weights")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(coef_selection_, interpolation="nearest", cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r)
plt.title("Feature Selection")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(coef_agglomeration_, interpolation="nearest", cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r)
plt.title("Feature Agglomeration")
plt.subplots_adjust(0.04, 0.0, 0.98, 0.94, 0.16, 0.26)
plt.show()
# Attempt to remove the temporary cachedir, but don't worry if it fails
shutil.rmtree(cachedir, ignore_errors=True)
Tiempo total de ejecución del script: (0 minutos 1.050 segundos)
